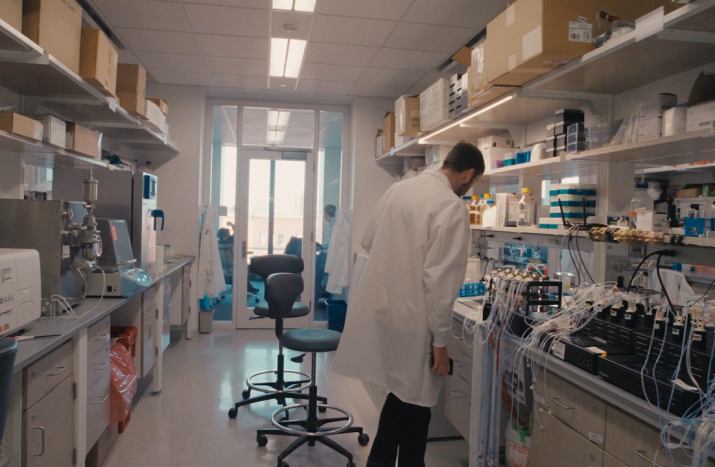
Brooklyn-based laboratory automation company Opentrons has launched its new Flex robot, designed to expand access to advanced laboratory automation for life scientists. In a recent email interview, Opentrons CEO Jonathan Brennan-Badal emphasized that the Opentrons Flex robot is designed to provide life scientists with a technologically advanced yet affordable automation platform. He noted that the bot is designed to perform a variety of experiments, including those designed by large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT.
AI-generated life science automation protocols
“It’s no exaggeration to say that LLM will revolutionize the way we design automation solutions in the life sciences,” explains Brennan-Badal. Opentrons’ compatibility with LLM makes it possible to “complement every documented manual experiment in the scientific literature.” It is now possible to create AI-generated automated protocols for every commercially available molecular biology kit. He believes that this ability will greatly affect the speed and scale of biological experiments.
Currently, developing and refining a single nucleic acid extraction protocol can take significant time, ranging from weeks to months, as researchers work to optimize variables such as sample type, DNA yield and quality, and reproducibility. “Using artificial intelligence can greatly improve this process,” Brennan-Badal said.
Flex is designed to support cost-effective laboratory automation
In addition to its focus on artificial intelligence, Opentrons is also aiming to compete for a place in the crowded laboratory automation space with established companies such as Labcyte, Tecan and Thermo Fisher Scientific by emphasizing economics and efficiency. "In terms of overall spend, Flex costs about one-tenth of the cost of similar products in its market," said Brennan-Badal, who attributes the cost reduction to the company's vertical integration in its manufacturing processes and supply chain management.
Brennan-Badal said the Flex robot is designed to be installed within a day. The system can be reconfigured in a short time by replacing pipettes and hardware modules. He attributes this modularity to product design, on-device display instructions and smart sensors that enable automatic calibration.
The company also designed Flex to have learning capabilities. Brennan-Badal explained that the robot’s open application programming interface (API) is compatible with the Design of Experiments program, including AI-driven agents, to support the development of future AI integrations.
“For software, we have a codeless protocol designer GUI, an open repository of verified and community-submitted protocols available for download, and a well-documented Python API for those who want ultimate control over their protocols or will People integrating third-party equipment or software with the robot,” Brennan-Badal said.
Artificial Intelligence in Laboratory Automation: Enhancing Flexibility and Experimental Design
One of the factors fueling interest in generative AI platforms is their ability to be coded in multiple languages. Brennan-Badal points out that Flex takes full advantage of this capability. "We have shown that LLMs, including ChatGPT 3.5 and 4, can write and correct executable Python code to automate experiments such as serial dilutions and aliquots on the Opentrons robot, and we are starting to get good data on more complex protocols," he explain.
"Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, led by Gabe Gomes, created an AI agent that combined LLM to design chemical synthesis experiments and then used these experimental designs as input to generate Python code to successfully run on Opentrons robots. Automate reactions,” Brennan-Badal noted. This research is highlighted in the preprint "Emerging Autonomous Scientific Research Capabilities for Large Language Models."
Opentrons' open and well-documented API is compatible with such programs. “LLM can be trained on Opentrons’ vast amounts of automation and protocol data to generate new automated experimental protocols,” asserts Brennan-Badal, noting that this capability future-proofs its platform’s ability to work within an AI framework.
Open source philosophy
Open source technology is a core element of the Flex robot's design, which could have implications for the scientific community. Brennan-Badal said an open source approach can support scientists by enabling platform development and integration and promoting protocols and knowledge sharing.
The open-source ethos of Flex Robots has significant implications for the scientific community. According to Brennan-Badal: “Open source supports scientists in two fundamental ways. It frees scientists to do new things, including building on platforms and integrating with other hardware and software. It facilitates the sharing of protocols and knowledge, allowing people around the world to scientists can replicate each other's work."
Brennan-Badal also highlighted the role Opentrons played early in the pandemic, noting how its automation capabilities streamlined laboratory workflows. He highlighted the use of the OT-2 model at Opentrons' outbreak response laboratory in New York City, where it has contributed to COVID sample processing.
Artificial Intelligence and Laboratory Automation Power the Future of Life Sciences
Looking ahead, the combination of artificial intelligence, especially large language models (LLMs), and laboratory automation may have an impact on the future of life sciences. Brennan-Badal believes that Opentrons' compatibility with LLM and the development of AI-generated automated protocols could impact the speed and scale of biological experiments.